Hello and welcome back to About Data And Finance! In my last post, I shared the pivotal moments that ignited my passion for personal finance. Today, we’re diving into one of the most crucial aspects: mortgage loans and interest rates.
Let’s rewind to where it all began – my mom’s financial troubles. Back in 2022, she found herself in a financial bind due to her variable-rate mortgage loan. I stepped in to help her navigate this crisis, only to realize that I had absolutely no clue about how mortgage loans and interest rates truly worked.
How Banks Make Profits
Banks, in their essence, make money by lending it. The money they lend must be repaid over time, with interest. It’s the interest that constitutes the bulk of the bank’s earnings. However, banks are good at hiding the importance of interest and people asking for a mortgage loan are very often unprepared.
The importance of the mortgage duration
When asking for a mortgage loan, there are two main parameters you should focus on:
1) The duration of the mortgage loan,
2) The interest rate applied by the bank.
The duration is decided by you. For example, you can decide whether repaying back your mortgage loan in 20 or 30 years. On the other hand, the interest rate is proposed by the bank, and you can either accept it or ask another bank. Although different banks can offer slightly different interest rates, all the European banks have to follow the European Central Bank (ECB) interest rates.
In today’s post we will focus on the importance of the duration of the mortgage loan.
In the next post we will focus on the importance of interest rates.
Calculating the monthly payment of a mortgage loan
Let’s consider the following situation:
You would like to buy a house in your favorite neighbor, which costs 275.000 euro. You have aside 25.000 euro for the down payment and some extra expenses. So, you ask your local bank a mortgage loan for 250.000 euro.
Under the current economic situation, the bank can offer a mortgage loan at a fixed rate of 4.5%.
Let’s simulate how much the monthly payment can vary depending on the mortgage duration (20, 25, 30, 35 and 40 years). For the simulations I am using a public tool of the Bank of Italy. I consider it simple and practical.
Now let’s look at the results (Figure 1).
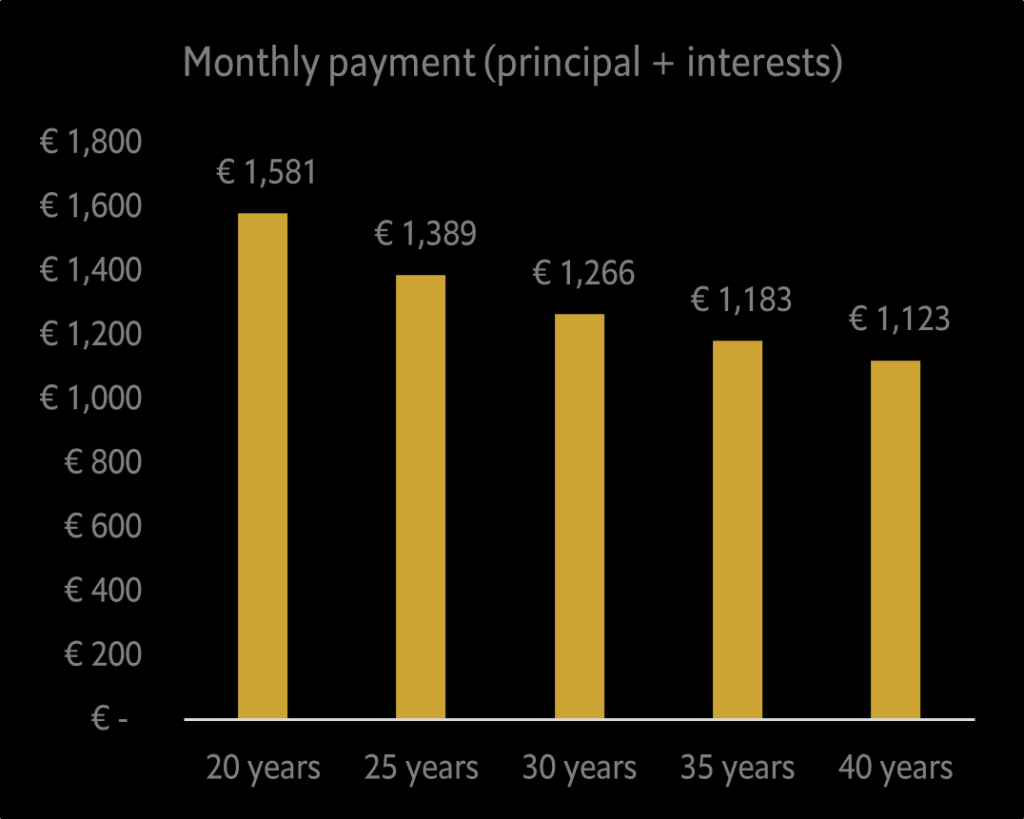
Figure 1: Monthly payment for different mortgage duration. Mortgage loan of 250.000 euro at 4.5% fixed-rate.
It is very clear that the longer the term of the mortgage loan, the lower the monthly payments will be. So, it is straightforward to opt for a 40-year duration.
However, not everyone knows that the monthly payment of a mortgage loan is made up of two components: the principal and the interest.
Calculating the total interests on a mortgage loan
Now, let’s have a look how much interests you will end up paying to the bank in each scenario (Figure 2).
Suddenly, the 40-year duration option does not look so convenient anymore. In this scenario you would pay back to the bank the 250.000 euro (the principal), plus 290.000 euro of interest, for a total of 540.000 euros (i.e. 1,123 euro x 12 months x 40 years).
In case you opt for the 20-year duration, the interest would be of 130.000 euro, leading to a saving of approximately 160.000 euro (= 290.000 euro – 130.000 euro).
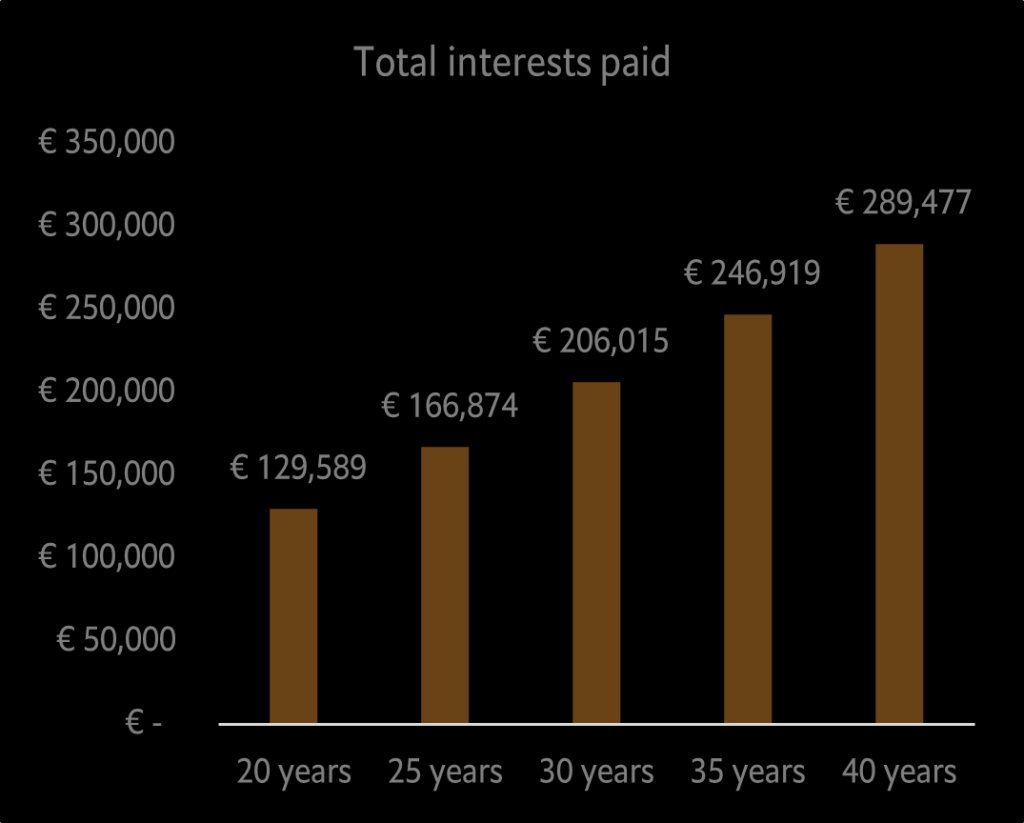
Figure 2: Total interests for different mortgage duration. Mortgage loan of 250.000 euro at 4.5% fixed-rate.
Rules we learnt
Two simple rules we can derive from looking at these simulations:
Rule 1: he shorter the term of the loan, the higher the monthly payments will be, but the amount owed in interests will be lower.
Rule 2: the longer the term of the loan, the lower the monthly payments will be, but the amount owed in interests will be higher.
Final recommendations and next topics
I recommend you play around with the simulator and tune it for your specific case. Just keep in mind the simulator works for a fixed-rate mortgage type only. The monthly payment and total interest of a variable-rate mortgage are more difficult to calculate since they can fluctuate based on the market conditions but for now, I’ll hit pause here.
In my next post, I’ll focus on another important parameter: the interest rate!
Stay tuned, and let’s continue this financial journey together!